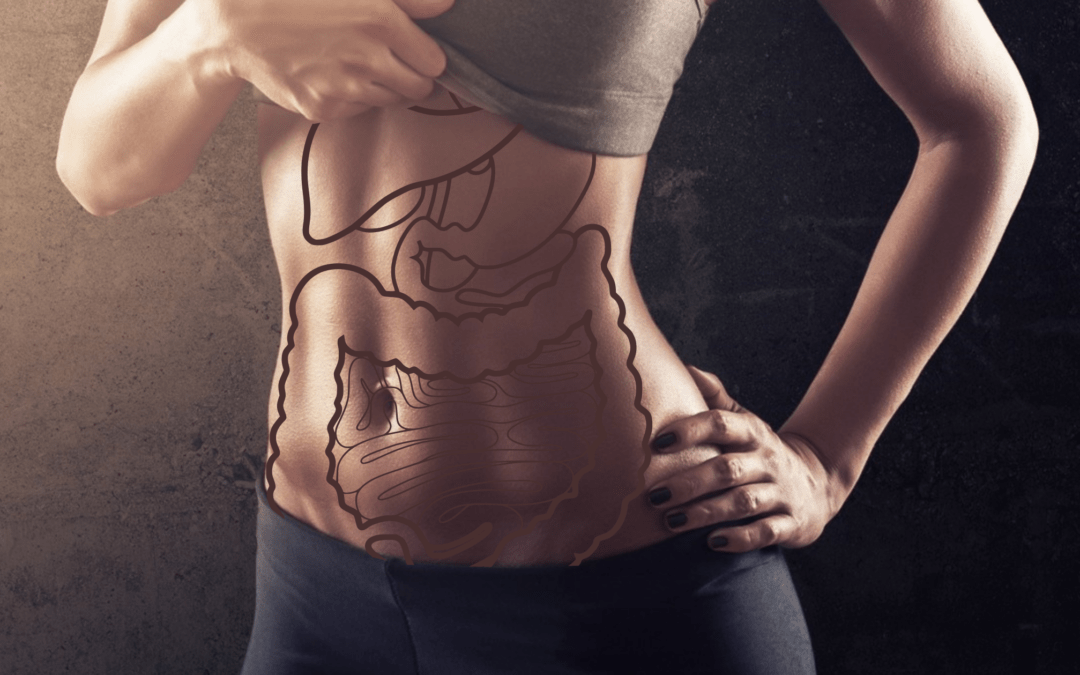
5 Ayurveda tips for GUT Health
5 Ayurveda tips for GUT Health
Our GUT or the digestive system is said to be the
” The SECOND BRAIN “.
 The health of the digestive organs their functionality and their physiology to transport the nutrition from the food to all the tissues of the body play a very vital role in the overall individual immunity and physical strength.
The health of the digestive organs their functionality and their physiology to transport the nutrition from the food to all the tissues of the body play a very vital role in the overall individual immunity and physical strength.
Ayurveda traditionally is known for the diet recommendations and GUT health rather than mere advice of treatment or symptomatic approach with herbal preparations.
Find below are the 5 best practices from the traditional text of Ayurveda recommended for a healthy DIGESTION.
Buttermilk / Takra
Takra or Buttermilk, as it is termed in Ayurveda text, is related as the best Nectar for all the functionality of the small intestines. The Buttermilk churned after the removal of the fat butter is very runny in consistency, sweety-sour to taste, and has a ratio of 1 part of Yogurt or Curd: 4 part warm water.
Buttermilk is one of the most beneficial foods which is widely used in India for centuries. In Ayurveda, a detailed description of different preparatory methods of Buttermilk is found to be having different properties and uses. Takra prepared by a proper method is useful for healthy people as well as for the ones suffering from different diseases. Different types of Buttermilk with spices and herbs can be prepared according to Dosaha involved. Regular intake of Buttermilk keeps a person healthy due to its Agnideepak & properties. According to Ayurveda Agnimandya is the root cause of any disease and Buttermilk is very useful in digestive problems.
Some of the recipes of Buttermilk Ayurveda preparations are as follows :
- Sour buttermilk 1 ounce + Dry ginger powder 1/4 tsp – for VATA problems
- Sour buttermilk 1 ounce+ Himalayan salt as to taste – for VATA problems
- Sweet buttermilk 1 ounce + brown sugar 1/2 tsp – for PITTA problems
- Sweet buttermilk 1 ounce + Trikatu powder 1/2 tsp ( Dry Ginger + Black Pepper + Long Medicinal Pepper)- for KAPHA problems
- Sweet buttermilk 1 ounce +Gud 1/2 tsp ( Jaggery ) – for Urinary problems
It is recommended to consume Buttermilk during the meal times for seven days, ten days, fifteen days, or one month according to the strength of the individual and the strength of a disease. The quantity of consumption of the Buttermilk should be in an increasing order till the maximum dose of 1 ounce and then should be decreased in the dose in a similar manner and never to be stopped at once.
Cumin / Jeeraka
Cuminum cyminum called Jeeraka in Sanskrit and Jeera in Hindi is one of the herbs which was used for many centuries for various ailments. Traditionally the herb is well-known for its action in various alimentary diseases like indigestion, diarrhea, gynecological diseases, etc. This herb is also screened for various pharmacological activities like antibacterial, anticancer, antiulcer, and others. Due to its hot potency and penetrative essential oils its a choice of the herb for the cure of various indications like Indigestion, Carminative, improve digestion, inflammations, diarrhea, noisy gut, but is directly establish it as a herb of choice in GIT associated menstrual disease.
In traditional medicine, cumin was used to treat hoarseness, jaundice, dyspepsia, and diarrhea. Its seeds were used for stomachic, diuretic, carminative, stimulant, astringent, and abortifacient properties. Due to its very good aroma, the oil of cumin was used in perfumery and as a seasoning in curry powders, soups, stews, sausages, cheeses, pickles, meats and chutneys since centuries in almost all part of the world.
In America, Africa and India the herb is used as an abortive and as an emmenagogue. In Indonesia, it was used in cases of bloody diarrhea and headache (the paste is applied to the forehead). It was also taken orally for rheumatic ailments. In India, cumin was used as an abortifacient, for kidney and bladder stones, chronic diarrhea, leprosy, and eye disease. In the Unani system of medicine, the fruits of the Cuminum cyminum were used as an astringent, carminative, emmenagogue, for the treatment of corneal opacities, ulcers, boils, styes and to relieve cough and inflammation.
Some of the recipes of Cumin Ayurveda preparations are as follows :
- Cumin powder (dry roasted) 1/4 tsp + Dry ginger powder 1/4 tsp + Natural honey 1 tsp – for Kapha problems or cough and congestion
- Cumin powder (dry roasted) 1/4 tsp + Jaggery 1tsp – for Digestion problems and low appetite
- Cumin powder (dry roasted) 1/4 tsp + Coriander seed powder (dry roasted ) 1/4 tsp + Hot water 1 cup – for cleansing the Urinary tract
- Cumin powder (dry roasted) 1/4 tsp + Lime juice 1 tsp – for Kapha and Vata problems
Ginger / Adraka
Ginger (Zingiber Officinalis), called Adraka in Sanskrit and Adrak in Hindi one of the most commonly consumed dietary condiments in the world. Ginger has been also been used for thousands of years for the treatment of numerous ailments, such as colds, nausea, arthritis, migraines, and hypertension. The medicinal, chemical, and pharmacological properties of ginger have been extensively reviewed by various institutions all around the world for its extensive medicinal usage and healing effects. Ginger is a member of a plant family that includes cardamom and turmeric. Its spicy aroma is mainly due to the presence of ketones, Gingerol.
Indians and Chinese are believed to have produced ginger as a tonic root for over 5000 years to treat many ailments, and this plant is now cultivated throughout the humid tropics, with India being the largest producer. Ginger was used as a flavoring agent long before history was formally recorded. It was an exceedingly important article of trade and was exported from India to the Roman Empire over 2000 years ago, where it was especially valued for its medicinal properties.
Ginger is used in numerous forms, including fresh, dried, pickled, preserved, crystallized, candied, and powdered or ground. The flavor is somewhat peppery and slightly sweet, with a strong and spicy aroma. The concentration of essential oils increases as ginger ages.
One of the many health claims attributed to ginger is its purported ability to decrease inflammation, swelling, and pain. Ginger decrease age-related oxidative stress markers and also due to its antioxidant properties help to reduce the free radicles. The essential oils in ginger help alleviating symptoms of nausea and vomiting throughout history is probably its utilization as the best remedy. Ginger and its derivative components have shown excellent and interesting cancer-preventive and potential cancer therapeutic applications. Ginger has gained interest for its potential to treat various aspects of cardiovascular disease. Useful for the treatment of various gastrointestinal, pulmonary, cardiovascular, sexual disorders, antibacterial, antidiabetic, antiemetic, hypolipidaemic, and hepatoprotective, Ginger is considered among the best of roots in Ayurveda.
Some of the recipes of Ginger Ayurveda preparations are as follows :
- Fresh ginger juice 1 tsp + Fresh holy basil leaves juice 1 tsp + Natural honey 1 tsp – for respiratory problems as dry cough, and Flatulence
- Fresh ginger paste + Jaggery – for sprains and inflammation without open wound (applied externally)
- Fresh ginger sliced + Hot water 1 cup – for lack of digestion, and Vata problems
- Fresh ginger juice + Brown sugar 1 tsp – for Kapha problems, common cold, and cough
Avoid Indigestion / Adhyashana
Adhyashana is a technical term of Ayurveda, which means eating before digestion of previous food. All the ancient classics describe the ill effects of Adhyashana. Charaka mentioned it as a prime causative factor for Grahani dosha. It is also said that Adhyashana can cause severe and incurable diseases or even death. All these references indicate the importance of Adhyashana as one of the health-destroying factors.
the food which is eaten, while the previous meal is lying undigested in the stomach, immediately provokes all the three Doshas. These aggravated Doshas then produce different kinds of diseases in the body. Repeated meals at irregular intervals are the very cause of Aama production ( free radicle ). Aama decreases the strength of Agni which in turn obstructs the free movement of all three Doshas in the digestive tract and on the other hand spreads in the whole body and blocks the channels of the entire body.
In a research conducted by an Institute in Jamnagar, India,70% of the subjects have revealed that lack of appetite and ingestions were the major pre disposed entity found among the patients with chronic lifestyle and infectious diseases such as fever of unknown origin, general lack of immunity, frequent infections of the chest and respiratory organs and skin diseases.
Adhyashana can be defined as eating within 3–4 h of the previous meal. So a proper light meal has to have at least a break of 4 hrs between each meal even considering snacks and coffee consumption. Drinking a small quantity of hot to warm water at regular intervals is said to have a positive effect on the digestive system hence aiding proper digestion.
Cleanse Free radicles / Ama
Ama iti Ishyath Pachyathe – meaning Ama or the free radicle are the product of indigestion. It is being described in one of the texts of Ayurveda that “eliminate that which is not wholeness, that which is disrupting, by that which is suitable for the self, using procedures and preparations to restore the self, to re-establish Prakriti (a wholeness — our essential nature) and pacify by that which is conducive to health.”
Ama can also be the one derived by the regular blockage of the free radicles in the deep channels of nutrition or even due to external environmental or idiopathic causes.
The main cause for the formation of Ama is described to be Pragya aparadh – the mistake of the intellect or the lack of self to understand our Dosha and body types and the capacity of our digestive systems. These very mistakes lead to poor diet, wrong choice of food, wrong eating habits, overeating, unnecessary cravings, emotional eating, and wrong routine.
The feel of laziness, disinterested, with no enthusiasm, lack of orientation, brain fog, lack of clarity, lack of concentration, negative thoughts, which can lead to anxiety and also Psychosomatic diseases such as bloating gut, lazy gut, constipation, IBS, diarrhea and many other diseases related to the Digestive system.
Some of the tips mentioned in Ayurveda text for cleaning the Ama are as follows :
- Loving your food with the right ingredient at the right time with the right state of mind or following Satvik food
- Avoid emotional eating. overeating, ice-cold food, heavy and sticky food
- Ama Pachan (digesting the ama ), by sipping hot water, or using specific spices or herbal preparations
- Agni Dipan (increasing the digestion ), with use of Lavana Bhasker powder, Cumin powder, Hingwashtaka powder
- Shodhana or Cleansing with Panchakarma Detox
- Home
- Special Offers
- AyurYoga Medic+
- AyurYoga Panchakarma
- Ananda Healing
- Burnout Prevention
- Wellness Escapes
- Pure Yoga Retreats
 No. 1 🏆 Ayurveda Resort in Thailand
No. 1 🏆 Ayurveda Resort in Thailand
Ayurveda in the Land of Smile 😊
The Mangosteen Ayurveda & Wellness Resort is the only family owned and managed Boutique Resort in Thailand, specialized in Ayurvedic Retreats. The resort is adult-only (12 years +) and proud to be a Member of Healing Hotels of the World, providing health holidays in a secluded tropical environment.
Experience the unique combination of the famous Thai hospitality with our Ayurveda expertise and a professional full-time team from Thailand and India.

Special offers for all retreats and accommodation
Take advantage of our best-price guarantee and book directly right here! 🤩 Low Season Special Offers, Discounts 🤩 Long Stay Offer 🤩 Early Bird Offer 🤩 Extra discount for higher deposit 🤩 Complimentary airport pickup More…

AyurYoga Medic+
Ayurveda healing with proven results For the ones looking for a science-backed traditional healing retreat with classic Ayurveda, combined with serological laboratory analysis for a proven record of the results. Retreat Summary: 🌹 Minimum 14 Nights for best and proven results 🌹 Arrival and departure serological laboratory analysis 🌹 Developed and guided by in-house doctor throughout the retreat period 🌹 About 2 hours daily Ayurveda treatments, 2 hours daily Yoga, all meals and drinks included More…
 AyurYoga Panchakarma Retreat
AyurYoga Panchakarma Retreat

Ananda Healing Retreat
Ayurveda – Reiki – Yoga – Meditation The Mangosteen Ananda Healing Retreat is a unique combination of several authentic Ayurveda treatments, Reiki healing sessions, Yoga, Meditation and prayers and other interesting, joyful experiences close to nature! Retreat Summary: 🌼 Minimum 3 Nights Retreat 🌼 Guided by in-house doctor throughout the retreat period 🌼 Experience our amazing Reiki Master 🌼 Sunrise Meditation, Temple visit, Ayurveda Experience 🌼 All meals and drinks included More…

Burnout Prevention Retreat
Prevention is better than cure! 🌻 7 nights / 8 days burnout prevention retreat 🌻 360 min. Spa treatments, 720 min Yoga & Meditation, 60 min Cardio or Zumba, 2x Magnesium Bath, approx. 130 min hiking/temple = over 22 hours active time and fun! 🌻 It’s so great, you can ask your boss to pay it 😂! More…
 Wellness Escape
Wellness Escape
4 Wellness Escapes, “Vigor”, “Vitalize”, “Relax” and “Toned”. Permanent Wellness Retreats with 2 daily Yoga Sessions! 🌷 Ongoing Yoga & Wellness Retreat with daily massages at our unique Ayurveda Spa. Book any dates! 🌷 2 hours daily yoga with our expert teachers. 🌷 3 nights minimum but stay as long as you wish. More….

Mangosteen Pure Yoga Retreats
Join Pure Yoga Retreats, starting from a minimum of 3 nights only. 🧘♂ Mangosteen Pure Yoga Retreats are ongoing, 365 days per year! 🧘♂ Join any day, any time and stay as long as you like. We are organizing beach yoga sessions, morning hikes and other activities. 🧘♂ Advanced yogis or beginners, we have the right class for you.
 The Mangosteen Team
The Mangosteen Team
Team Mangosteen, a skilled team with plenty of experience, takes care of all your daily fun, healthy activities, your comfort, and enjoyment.
Meet the teachers, Meet the spa team, Meet the owners!
😎 Have a closer look at team Mangosteen!
 The Green Resort
The Green Resort
Our comprehensive environmental concept
🌴 Nowadays everyone is speaking about sustainability and environmental impact, we did before we even started planning the resort. Mangosteen has been planned as a “green resort” since day one.
🌴 Have a look at the list of features and how we manage one of the greenest resorts on the Island.
- Ayurveda
- Why Ayurveda
- 🧘♂️ AyurYoga Medic+
- 🧘♂️ AyurYoga Panchakarma
- 🧘♂️ AyurYoga Sampoorna
- AyurYoga Wellbeing
- Ananda Healing
- Virus & Flu Prevention
- Ayurveda Herbal Garden
- Dosha Form
 Ayurveda
Ayurveda
Ayurvedic medicine (“Ayurveda” for short) is one of the world’s oldest holistic (“whole-body”) healing systems. It is a system that was developed more than 3,000 years ago in India and since improved and perfected to the state it is known for today. It’s based on the belief that health and wellness depend on a delicate balance between the mind, body, and spirit.
Its main goal is to promote good health, not to fight disease.
 Why Ayurveda?
Why Ayurveda?
Hectic life in modern society mostly ignores traditional, natural, holistic healing methods. Ayurveda is an ancient holistic healing method from India, taking numerous factors of your body, your “Doshas” into account.
Many people are realizing that classic medicine often produces more side effects than effects, relating increasingly to traditional, natural healing methods.

AyurYoga Medic+
Ayurveda healing with proven results
For the ones looking for a science-backed traditional healing retreat with classic Ayurveda, combined with serological laboratory analysis for a proven record of the results.
Retreat Summary:
🌹 Minimum 14 Nights for best and proven results
🌹 Arrival and departure serological laboratory analysis
🌹 Developed and guided by in-house doctor throughout the retreat period
🌹 About 2 hours daily Ayurveda treatments, 2 hours daily Yoga, all meals and drinks included
AyurYoga Panchakarma
The classic, authentic Ayurveda Retreats!
The Mangosteen Ayurveda & Wellness Resort brought authentic Ayurveda to Thailand. We are combining an amazing holiday experience on the beautiful Island of Phuket with the best Ayurveda Panchakarma Retreat, daily Yoga, healthy Satvik-Meals – enjoyable and unforgettable!
Experience the unique combination of the famous Thai hospitality with our Ayurveda expertise and a professional full-time team from Thailand and India.
Retreat Summary:
🌷 Minimum 7 Nights Ayurveda Panchakarma Retreats
🌷 Guided by in-house doctor throughout the retreat period
🌷 About 2 hours daily Ayurveda treatments
🌷 2 hours daily Yoga, access to Himalayan Rock Salt Infrared Sauna

AyurYoga Sampoorna
Ayurveda Panchakarma Retreat for complete healing of body and mind!
Retreat Summary:
🌻 Minimum 14 Nights Ayurveda Panchakarma Retreats
🌻 Guided by in-house doctor throughout the retreat period
🌻 First week 1-hour daily treatments, remaining time 2-hours daily Ayurveda treatments
🌻 2 hours daily Yoga, access to Himalayan Rock Salt Infrared Sauna

Ayurveda Wellbeing Retreat
Ayurveda Longstay Retreat for general Wellbeing
Ayurveda Wellbeing is for the ones seeking a healthy holiday break with traditional healing and all other indulgence and experiences from deep within, to balance the EMOTIONS, PHYSICAL ENERGIES, STRESS, and total FUNCTIONALITY.
Retreat Summary:
🌻 Minimum 28 Nights Ayurveda Wellbeing Retreat
🌻 Ideal for longstay relaxation, combined with Ayurveda
🌻 Temple meditation, several hiking trips, Ayurveda treatments
🌻 2 hours daily Yoga, access to Himalayan Rock Salt Infrared Sauna
🌻 All meals and life-drinks included

Ananda Healing Retreat
Ayurveda – Reiki – Yoga – Meditation
The Mangosteen Ananda Healing Retreat is a unique combination of several authentic Ayurveda treatments, Reiki healing sessions, Yoga, Meditation and prayers and other interesting, joyful experiences close to nature!
Retreat Summary:
🌼 Minimum 3 Nights Retreat
🌼 Guided by in-house doctor throughout the retreat period
🌼 Experience our amazing Reiki Master
🌼 Sunrise Meditation, Temple visit, Ayurveda Experience
🌼 All meals and drinks included
 Virus & Flu Prevention
Virus & Flu Prevention
Ayurveda Cleansing Methodologies
FLU and VIRUS infections to the respiratory tract have been quite a common infestation and history since the existence of mankind.
The potency of the Virus is strongest during the peak of the winters and the change in climatic conditions, when the immune system is at the weakest.
It’s the very nature of a virus to create a better self each year, with a better characteristic and a stronger new generation every year, and the only defense that can destroy them is the strong human body itself with the symptoms of fever, headache, nasal and oral discharges.
The Ayurvedic Herbal Pharmacy
🌿 Ayurvedic herbs are the key for Ayurveda, the traditional, natural medicine from India. Our Ayurveda Spa Team uses ayurvedic herbs to “cleanse” the body, boost immunity against disease, and keep the mind, body, and spirit in balance.
🌿 Walk around the resorts large garden and find many of the herbs, we are using.
Here is the MAP with all the information.
 Ayurveda Dosha Consultation Form
Ayurveda Dosha Consultation Form
Nature has its origin and evolves in the presence of ELEMENTS such as ether, air, fire, water, and earth. These elements put together embodiment characters called DOSHA which form the core of Ayurveda science.
Hence to establish an ideal approach in treating the Mind, Body and the Soul, the involvement of the Dosha must be pictured in detail.
- Wellness & Spa
- 🏆 Reward of Life
- 🍉 Juicing & Raw Food
- 🏃♂️ Wellness Escape
- Weekend Retreat
- 🔥 Burnout Prevention
- Algotherm Slim & Firm
 Wellness & Spa
Wellness & Spa
🧘♂️ What defines the Mangosteen as a Wellness Resort?
🧘♂️ An overview of our different retreat programs.
🧘♂️ Ayurveda, Burnout Prevention, Meditation and Yoga. Select your ideal retreat!
 Reward of Life
Reward of Life
💚 2 Nights / 3 Days Retreat full of activities, including Yoga, Massages, Healthy Meals, and Drinks.
Take a Break to quick charge your batteries!
💚 Reward yourself with a healthy, fun holiday break
💚 “Reward of Life” – The Yoga & Wellness Retreat

Juicing & Raw Food Retreat
5 nights, 6 days – Cleansing – Juicing and Raw Food Retreat
🍉 Comprehensive 5 nights Cleansing and Detox Program, a transformative journey designed to rejuvenate your body, mind, and spirit.
🍉 55 min. Balancing Massage, 2 hours daily yoga with our expert teachers.
🍉 Extend stay by combining with other retreat programs, f. e. Pure Yoga or Wellness Escape
 Wellness Escape
Wellness Escape
4 Wellness Escapes, “Vigor”, “Vitalize”, “Relax” and “Toned”.
Permanent Wellness Retreats with 2 daily Yoga Sessions!
🌷 Ongoing Yoga & Wellness Retreat with daily treatments at our unique Ayurveda Spa. Book any dates!
🌷 2 hours daily yoga with our expert teachers.
🌷 3 nights minimum but stay as long as you wish.
 Weekend Retreat
Weekend Retreat
An active, healthy, all-inclusive weekend in Rawai, Phuket
🌺 3 nights: Check-in on Thursday and stay until Sunday!
🌺 Many amazing inclusions:
- Morning Hike / Walk
- Ayurveda Spa treatment and massages
- Cardio Workout or Zumba Dance
- Magnesium bath, deep relaxation
- Singing Bowl & Chakra Meditation
 Burnout Prevention Retreat
Burnout Prevention Retreat
Prevention is better than cure!
🌻 7 nights / 8 days burnout prevention retreat
🌻 360 min. Spa treatments, 720 min Yoga & Meditation, 60 min Cardio or Zumba, 2x Magnesium Bath, approx. 130 min hiking/temple = over 22 hours active time and fun!
🌻 It’s so great, you can ask your boss to pay it 😂!
 Algotherm Slim & Firm
Algotherm Slim & Firm
DISCOVER THE RICHNESS OF THE ALGAE AND MARVEL AT THE POWER OF NATURE
🌿 5 effective marine complexes exclusive to results demonstrated on the skin.
🌿 6 day Slim & Firm program, best results in short time
🌿 Enjoy an original Algotherm program in beautiful environment during your Wellness holiday.
 Activities
Activities
The resort team organizes activities outside of the normal schedule quite frequently.
🧘♂️ Please check this page regularly. A QR Code, leading to this page is displayed at our reception and at the spa. Leave the browser tab open throughout your stay with us!
🧘♂️We update the calendar daily, so you know who the teachers are, when we organize a beach Yoga session, when we offer additional meditation classes or when we go hiking.
Additional Activities & Consultants
The Mangosteen has a large team of qualified, experienced advisors, coaches, and consultants available for you.
Define your clear goals and plan your wellness journey in the best possible manner. Please contact our Wellness Coordinator at the Spa if you are interested in adding some of the sessions to further enhance your stay.
🤸♂️ Let us help you get the best results.

Nutrition
Using the best and healthiest ingredients only, the Mangosteen Chef’s also spoil your taste buds
🥕 Ayurveda cuisine with a Thai influence
🥕 Vegan meals with veggies partly from our own garden, daily Life-Drinks.
🥕 We are what we Eat
 Ayurveda Cuisine
Ayurveda Cuisine
Ayurveda & Six Tastes (Shad Rasas)
🥒 Eating healthy with variety, taste, and phantasy. Let us surprise you!
🥒 Dosha neutral meals that support your detoxification process.
🥒 Why is everybody asking us for the recipes? 😃
 Vegan Cuisine
Vegan Cuisine
Delicious, so you won’t miss anything, even if you are not used to vegan cuisine.
🍅 A well balanced, tasty diet that simply is good for you.
🍅 Herbs and spices are vegan too!
🍅 Need something different sometimes? No worries, simply choose from our alternative menu.
 Life Drinks
Life Drinks
Life-Drinks, Super-Drinks and Smoothie Blends
🍹 The Life-Drinks are part of your daily Wellness Program, assisting your body in the process of rejuvenating, feeling refreshed and energized.
🍹 Smoothie-Blends, delicious energy boosters, full of vitamins and taste!

Mangosteen Resort
The No. 1 Ayurveda & Wellness Resort in Thailand!
🌴 Boutique Resort with 50 tropical Villas, family owned and managed.
🌴 Adult-only (12 years +) for peaceful and quiet atmosphere.
🌴Located on a hillside with amazing sea views, in the center of Rawai, Phuket’s popular holiday destination with a local flair.

The Spa Facilities
For the benefit of your health and pleasure, the resort offers the following features:
🌺 Steam Saunas
🌺 Himalaya Rock-Salt Infrared Sauna
🌺 Tourmaline & Germanium Stone Far-Infrared Dome Sauna
🌺 Magnesium Bath Jacuzzi
🌺 Ice Tub (Coming soon)
🌺 Fitness Room
🌺 Prana Yoga Sala & Ananda Yoga Room
🌺 Veda Villa
🌺 Ayurveda Herbs Supply (Coming soon)
Relax and rejuvenate at the Mangosteen Resort!
The Area – Mangosteen Neighborhoods
The South of Phuket offers the best beaches, viewpoints, hikes, seafood, sunsets and culture.
🌴 Nai Harn Beach & Promthep Cape Sunset Viewpoint
🌴 Viewpoints, Krating Cape, Black Rock etc.
🌴 Chalong and Rawai Bay & Seafood Market
🌴 The Phuket Big Buddha & Chalong Temple
And a lot more! Have a look at our dedicated page which describes the area and offers many ideas for activities.

Mangosteen Day Passes
Spend a day at the Mangosteen Ayurveda & Wellness Resort, even if you don’t stay there.
We offer several individual Day Passes:
🌴 Yoga Privilege Day Pass
🌴 Wellness Day Pass
🌴 Weekend Day Pass
🌴 Comprehensive Day Pass
They are based on credit, no fee or offer many inclusions, such as the Wellness Escape Retreat.

The Ayurveda Spa Menu
By far Asia’s largest choice of Ayurveda treatments!
💆♀️ Ancient Ayurveda treatments nowhere else available.
💆♀️ Veda Villa, the most specialized Ayurvedic menu, performed by experts.
Mangosteen Ayurveda & Wellness Resort
Get in Touch

Contact Info
Address
99/4 Moo 7, T. Rawai, A. Muang
Phuket 83130, Thailand
Telephone
Line-ID
Follow On
Mangosteen Ayurveda & Wellness Resort

Kontakt Info
Adresse
99/4 Moo 7, T. Rawai, A. Muang
Phuket 83130, Thailand
Telefon
+66 76 289399
+66 91 0415615
Line-ID
Folgt uns auf
Neuigkeiten vom Mangosteen Resort
Gesundheitsblog mit nützlichen Informationen und Neuigkeiten rund um das Ayurveda Spa
🗞️ Mangosteen Ayurveda Blog mit Expertenwissen unseres Ayurveda Spa-Teams.
🗞️ Neuigkeiten aus dem Mangosteen Ayurveda Spa, allgemeine Gesundheitstipps und weitere nützliche Informationen, regelmäßig aktualisiert.

Mangosteen Resort
Das Ayurveda- und Wellness-Resort Nr. 1 in Thailand!
🌴 Boutique-Resort mit 50 tropischen Villen, 100% im Familienbesitz, geführt von der Familie.
🌴 Nur für Erwachsene (ab 12 Jahren) für eine friedliche und ruhige Atmosphäre.
🌴Auf einem Hügel mit herrlichem Meerblick gelegen, im Zentrum von Rawai, Phukets beliebtem Urlaubsziel mit lokalem Flair.
 Die Spa-Einrichtungen
Die Spa-Einrichtungen
Zum Wohle Ihrer Gesundheit und Ihres Vergnügens bietet das Resort folgende Leistungen:
🌺 Dampfsaunen
🌺 Himalaya-Steinsalz-Infrarotsauna
🌺 Turmalin- und Germaniumstein-Ferninfrarot-Kuppelsauna
🌺 Magnesiumbad-Whirlpool
🌺 Eisbad (in Planung))
🌺 Fitnessraum
🌺 Prana Yoga Sala & Ananda Yoga Raum
🌺 Veda Villa (Ayurveda Behandlungsräume)
🌺 Ayurveda-Kräuterversorgung
Entspannen und erholen Sie sich im Mangosteen Resort!
 Die Umgebung – Mangosteen Nachbarschaft
Die Umgebung – Mangosteen Nachbarschaft
Der Süden von Phuket bietet die besten Strände, Aussichtspunkte, Wanderungen, Meeresfrüchte, Sonnenuntergänge und Kultur.
🌴 Nai Harn Beach und Aussichtspunkt Promthep Cape Sunset
🌴 Aussichtspunkte, Krating Cape, Black Rock usw.
🌴 Chalong und Rawai Bay & Meeresfrüchtemarkt
🌴 Der Phuket Big Buddha und der Chalong-Tempel
Und vieles mehr! Werfen Sie einen Blick auf unsere spezielle Seite, die die Gegend beschreibt und viele Ideen für Aktivitäten bietet.
Mangosteen-Tageskarten
Verbringen Sie einen Tag im Mangosteen Ayurveda & Wellness Resort, auch wenn Sie nicht dort übernachten.
Wir bieten mehrere individuelle Tageskarten an:
🌴 Yoga Privilege Day Pass
🌴 Wellness-Tageskarte
🌴 Wochenend-Tageskarte
🌴 Umfassender Tagespass
Sie basieren auf Guthaben, sind gebührenfrei oder bieten viele Inklusivleistungen, wie zum Beispiel das Wellness Escape Retreat.

Ernährung
Die Mangosteen Chef’s verwenden ausschließlich die besten und gesündesten Zutaten und verwöhnen auch Ihren Gaumen
🥕 Ayurveda-Küche mit thailändischem Einfluss
🥕 Vegane Mahlzeiten mit Gemüse teilweise aus unserem eigenen Garten, tägliche Life-Drinks.
🥕 Wir sind, was wir essen
 Ayurveda-Küche
Ayurveda-Küche
Ayurveda und sechs Geschmacksrichtungen (Shad Rasas)
🥒Gesund ernähren mit Abwechslung, Geschmack und Fantasie. Lassen Sie sich überraschen!
🥒 Dosha-neutrale Mahlzeiten, die Ihren Entgiftungsprozess unterstützen.
🥒 Warum fragen uns alle nach den Rezepten? 😃
 Vegane Küche
Vegane Küche
Lecker, sodass es Ihnen an nichts fehlt, auch wenn Sie die vegane Küche nicht gewohnt sind.
🍅 Eine ausgewogene, schmackhafte Ernährung, die einfach guttut.
🍅 Auch Kräuter und Gewürze sind vegan!
🍅 Brauchen Sie manchmal etwas anderes? Keine Sorge, wählen Sie einfach aus unserem alternativen Menu.
 Life Drinks
Life Drinks
Life-Drinks, Super-Drinks und Smoothie-Mischungen
🍹 Die Life-Drinks sind Teil Ihres täglichen Wellness-Programms und unterstützen Ihren Körper dabei, sich zu regenerieren, sich erfrischt und voller Energie zu fühlen.
🍹 Smoothie-Mischungen, leckere Energie-Booster, voller Vitamine und Geschmack!
 Aktivitäten
Aktivitäten
Das Resort Team organisiert häufig Aktivitäten außerhalb des normalen Zeitplans.
🧘♂️ Bitte schauen Sie regelmäßig auf dieser Seite vorbei. Ein QR-Code, der zu dieser Seite führt, wird an unserer Rezeption und im Spa angezeigt. Lassen Sie den Browser-Tab während Ihres Aufenthalts bei uns geöffnet!
🧘♂️ Noch besser: Installieren Sie die “Mangosteen Ayurveda” Applikation, um zusätzliche Benachrichtigungen zu erhalten. So sind Sie immer im Bilde.
🧘♂️Wir aktualisieren den Kalender täglich, damit Sie wissen, wer die Lehrer sind, wenn wir eine Strand-Yoga-Sitzung organisieren, wenn wir zusätzliche Meditationskurse anbieten oder wenn wir wandern gehen.
Zusätzliche Aktivitäten und Berater

The Mangosteen verfügt über ein großes Team qualifizierter, erfahrener Berater, Coaches und Consultants, die für Sie da sind.
Definieren Sie klare Ziele und planen Sie Ihre Wellness-Reise bestmöglich. Bitte wenden Sie sich an unseren Wellness-Koordinator im Spa, wenn Sie daran interessiert sind, einige der Sitzungen hinzuzufügen, um Ihren Aufenthalt noch angenehmer zu gestalten.
🤸♂️ Lassen Sie uns Ihnen helfen, die besten Ergebnisse zu erzielen.
- Wellness & Spa
- 🏆 Reward of Life
- 🍉 Juicing & Rohkost
- 🏃♂️ Wellness Escape
- Wochenend-Retreat
- 🔥 Burnout Prävention
- Algotherm Slim & Firm
 Wellness & Spa
Wellness & Spa
🧘♂️ Was macht das Mangosteen als Wellness-Resort aus?
🧘♂️ Ein Überblick über unsere verschiedenen Retreat-Programme.
🧘♂️ Ayurveda, Burnout-Prävention, Juicing & Rohkost, Meditation und Yoga. Wählen Sie Ihr ideales Retreat!
 Reward of Life
Reward of Life
💚 2 Nächte / 3 Tage Retreat voller Aktivitäten, darunter Yoga, Massagen, gesunde Mahlzeiten und Getränke. Machen Sie eine Pause, um Ihre Batterien schnell aufzuladen!
💚 Belohnen Sie sich mit einem gesunden und unterhaltsamen Urlaub
💚 „Reward of Life“ – Das Yoga & Wellness Retreat

Juicing & Rohkost Retreat
5 Nächte, 6 Tage – Reinigungs-, Juicing und Rohkost-Retreat
🍉 Umfassendes 5-Nächte-Reinigungs- und Entgiftungsprogramm, eine transformative Reise zur Verjüngung von Körper, Geist und Seele.
🍉 55 Min. Balancing Massage, täglich 2 Stunden Yoga mit unseren erfahrenen Yoga-Lehrern.
🍉 Verlängern Sie den Aufenthalt durch die Kombination mit anderen Retreat-Programmen, z. e. Pure Yoga oder Wellness Escape oder auch unserem Klassiker, AyurYoga Panchakarma.
 Wellness Escape
Wellness Escape
4 Wellness-Retreats: „Vigor“, „Vitalize“, „Relax“ und „Toned“.
Permanente Wellness-Retreats mit 2 täglichen Yoga-Sitzungen!
🌷 Laufendes Yoga- und Wellness-Retreat mit täglichen Behandlungen in unserem einzigartigen Ayurveda-Spa. Buchen Sie beliebige Daten!
🌷 2 Stunden tägliches Yoga mit unseren erfahrenen Lehrern.
🌷 Mindestens 3 Nächte, aber bleiben Sie so lange, wie Sie möchten.
 Wochenend-Retreat
Wochenend-Retreat
Ein aktives, gesundes All-Inclusive-Wochenende in Rawai, Phuket
🌺 3 Nächte: Check-in am Donnerstag und Aufenthalt bis Sonntag!
🌺 Viele großartige Inklusivleistungen:
- Morgenwanderung / Spaziergang
- Ayurveda-Spa-Behandlung und Massagen
- Cardio-Training oder Zumba-Tanz
- Magnesiumbad, Tiefenentspannung
- Klangschalen- und Chakra-Meditation
 Burnout Prävention Retreat
Burnout Prävention Retreat
Vorbeugung ist besser als Heilung!
🌻 7 Nächte / 8 Tage Burnout-Präventions-Retreat
🌻 360 Min. Spa-Behandlungen, 720 Min. Yoga & Meditation, 60 Min. Cardio oder Zumba, 2x Magnesiumbad, ca. 130 Minuten Wandern/Tempel = über 22 Stunden aktive Zeit und Spaß!
🌻 Es ist so toll, dass Sie Ihren Chef bitten können, es zu bezahlen 😂!
 Algotherm Slim & Firm
Algotherm Slim & Firm
ENTDECKEN SIE DEN REICHHALT DER ALGEN UND STAUNEN SIE ÜBER DIE KRAFT DER NATUR
🌿 5 wirksame Meereskomplexe, die ausschließlich nachweisbare Ergebnisse auf der Haut erzielen.
🌿 6-tägiges Slim & Firm-Programm, beste Ergebnisse in kurzer Zeit
🌿 Genießen Sie in Ihrem Wellnessurlaub ein originelles Algotherm-Programm in wunderschöner Umgebung.
- Ayurveda
- Warum Ayurveda
- 🧘♂️ AyurYoga Medic+
- 🧘♂️ AyurYoga Panchakarma
- 🧘♂️ AyurYoga Sampoorna
- Ayurveda Wellbeing Retreat
- Ananda Healing
- Virus & Flu Prävention
- Ayurvedische Kräuterapotheke
- Dosha Auskunftsformular
 Ayurveda
Ayurveda
Die ayurvedische Medizin (kurz „Ayurveda“) ist eines der ältesten ganzheitlichen („Ganzkörper“)- Heilsysteme der Welt. Es handelt sich um ein System, das vor mehr als 3.000 Jahren in Indien entwickelt und seitdem zu dem Stand verbessert und perfektioniert wurde, für den es heute bekannt ist. Es basiert auf der Überzeugung, dass Gesundheit und Wohlbefinden von einem empfindlichen Gleichgewicht zwischen Geist, Körper und Seele abhängen.
Ihr Hauptziel ist die Förderung der Gesundheit und nicht die Bekämpfung von Krankheiten.
 Warum Ayurveda?
Warum Ayurveda?
Das hektische Leben in der modernen Gesellschaft lässt traditionelle, natürliche und ganzheitliche Heilmethoden meist außer Acht. Ayurveda ist eine uralte ganzheitliche Heilmethode aus Indien, die zahlreiche Faktoren Ihres Körpers, Ihre „Doshas“, berücksichtigt.
Viele Menschen erkennen, dass die klassische Medizin oft mehr Nebenwirkungen als Wirkungen hat und wenden sich zunehmend traditionellen, natürlichen Heilmethoden zu.

AyurYoga Medic+
Ayurveda-Heilung mit nachweisbaren Ergebnissen
Für diejenigen, die auf der Suche nach einem wissenschaftlich fundierten traditionellen Heilretreat mit klassischem Ayurveda sind, kombiniert mit serologischen Laboranalysen zur nachweisbaren Aufzeichnung der Ergebnisse.
Zusammenfassung des Retreats:
🌹 Mindestens 14 Nächte für beste und bewährte Ergebnisse
🌹 Serologische Laboranalyse bei Ankunft und Abreise
🌹 Entwickelt und begleitet vom hauseigenen Arzt während der gesamten Retreat-Zeit
🌹 Etwa 2 Stunden täglich Ayurveda-Behandlungen, 2 Stunden täglich Yoga, alle Mahlzeiten und Getränke inklusive
AyurYoga Panchakarma
Die klassischen, authentischen Ayurveda-Retreats!
Das Mangosteen Ayurveda & Wellness Resort brachte authentisches Ayurveda nach Thailand. Wir kombinieren ein fantastisches Urlaubserlebnis auf der wunderschönen Insel Phuket mit dem besten Ayurveda-Panchakarma-Retreat, täglichem Yoga und gesunden Satvik-Mahlzeiten – angenehm und unvergesslich!
Erleben Sie die einzigartige Kombination der berühmten thailändischen Gastfreundschaft mit unserer Ayurveda-Expertise und einem professionellen Vollzeitteam aus Thailand und Indien.
Zusammenfassung des Retreats:
🌷 Mindestens 7 Nächte Ayurveda-Panchakarma-Retreats
🌷 Begleitung durch den hauseigenen Arzt während der gesamten Retreat-Zeit
🌷 Ca. 2 Stunden täglich Ayurveda-Behandlungen
🌷 2 Stunden täglich Yoga, Zugang zur Himalaya-Steinsalz-Infrarotsauna

AyurYoga Sampoorna
Ayurveda-Panchakarma-Retreat für die vollständige Heilung von Körper und Geist!
Zusammenfassung des Retreats:
🌻 Mindestens 14 Nächte Ayurveda-Panchakarma-Retreats
🌻Betreuung durch einen hauseigenen Arzt während der gesamten Retreat-Zeit
🌻 Erste Woche 1-stündige tägliche Behandlungen, verbleibende Zeit 2-stündige tägliche Ayurveda-Behandlungen
🌻 2 Stunden täglich Yoga, Zugang zur Himalaya-Steinsalz-Infrarotsauna

Ayurveda Wellbeing Retreat
Ayurveda-Longstay-Retreat für allgemeines Wohlbefinden
Ayurveda Wellbeing ist für diejenigen gedacht, die einen gesunden Urlaub mit traditioneller Heilung und allen anderen Verwöhnprogrammen und Erfahrungen aus tiefstem Inneren verbringen möchten, um EMOTIONEN, PHYSIKALISCHE ENERGIEN, STRESS und die gesamte FUNKTIONALITÄT auszugleichen.
Zusammenfassung des Retreats:
🌻 Mindestens 28 Nächte Ayurveda-Wellness-Retreat
🌻 Ideal für Langzeitentspannung, kombiniert mit Ayurveda
🌻 Tempelmeditation, mehrere Wanderausflüge, Ayurveda-Behandlungen
🌻 2 Stunden täglich Yoga, Zugang zur Himalaya-Steinsalz-Infrarotsauna
🌻 Alle Mahlzeiten und Life-Drinks inklusive

Ananda Healing Retreat
Ayurveda – Reiki – Yoga – Meditation
Das Mangosteen Ananda Healing Retreat ist eine einzigartige Kombination aus mehreren authentischen Ayurveda-Behandlungen, Reiki-Heilsitzungen, Yoga, Meditation und Gebeten sowie anderen interessanten, freudigen Erlebnissen in der Nähe der Natur!
Zusammenfassung des Retreats:
🌼 Mindestens 3 Nächte Retreat
🌼 Begleitung durch den hauseigenen Arzt während der gesamten Retreat-Zeit
🌼 Erleben Sie unseren erstaunlichen Reiki-Meister
🌼 Sonnenaufgangsmeditation, Tempelbesuch, Ayurveda-Erlebnis
🌼 Alle Mahlzeiten und Getränke inklusive
 Virus & Flu Prävention
Virus & Flu Prävention
Ayurveda-Reinigungsmethoden
Grippe- und Virusinfektionen der Atemwege sind ein weit verbreiteter Befall und haben seit der Existenz der Menschheit eine lange Geschichte.
Die Wirksamkeit des Virus ist während der Hochsaison im Winter und bei wechselnden klimatischen Bedingungen am stärksten, wenn das Immunsystem am schwächsten ist.
Es liegt in der Natur eines Virus, jedes Jahr ein besseres Selbst zu erschaffen, mit besseren Eigenschaften und jedes Jahr eine stärkere neue Generation, und die einzige Verteidigung, die sie zerstören kann, ist der starke menschliche Körper selbst mit den Symptomen Fieber, Kopfschmerzen, Nase und orale Entladungen.
Die ayurvedische Kräuterapotheke
🌿 Ayurveda-Kräuter sind der Schlüssel für Ayurveda, die traditionelle, natürliche Medizin aus Indien. Unser Ayurveda-Spa-Team verwendet ayurvedische Kräuter, um den Körper zu „reinigen“, die Immunität gegen Krankheiten zu stärken und Geist, Körper und Seele im Gleichgewicht zu halten.
🌿 Spazieren Sie durch den großen Garten des Resorts und finden Sie viele der Kräuter, die wir verwenden.
Hier ist die KARTE mit allen Informationen.
 Ayurveda Dosha Auskunftsformular
Ayurveda Dosha Auskunftsformular
Die Natur hat ihren Ursprung und entwickelt sich in der Gegenwart von ELEMENTEN wie Äther, Luft, Feuer, Wasser und Erde. Diese Elemente bilden die Verkörperungscharaktere namens DOSHA, die den Kern der Ayurveda-Wissenschaft bilden.
Um einen idealen Ansatz für die Behandlung von Geist, Körper und Seele zu finden, muss daher die Beteiligung des Dosha im Detail dargestellt werden.
 Das Mangosteen-Team
Das Mangosteen-Team
Team Mangosteen, ein kompetentes Team mit viel Erfahrung, kümmert sich um all Ihren täglichen Spaß, gesunde Aktivitäten, Ihren Komfort und Ihr Vergnügen.
Treffen Sie die Lehrer, treffen Sie das Spa-Team, treffen Sie die Besitzer!
😎 Schauen Sie sich das Team Mangosteen genauer an!
 Das Grüne Resort
Das Grüne Resort
Unser umfassendes Umweltkonzept
🌴 Heutzutage sprechen alle über Nachhaltigkeit und Umweltauswirkungen, und das taten wir schon, bevor wir überhaupt mit der Planung des Resorts begonnen haben. Mangosteen wurde vom ersten Tag an als „grünes Resort“ geplant.
🌴 Werfen Sie einen Blick auf die Liste der Umwelt-Eigenschaften und wie wir eines der grünsten Resorts der Insel verwalten.
- Home
- 🔥 Angebote
- AyurYoga Medic+
- AyurYoga Panchakarma
- Ananda Healing
- Burnout Prevention
- Wellness Escapes
- Pure Yoga Retreats
 No. 1 🏆 Ayurveda Resort in Thailand
No. 1 🏆 Ayurveda Resort in Thailand
Ayurveda im Land des Lächelns 😊
Das Mangosteen Ayurveda & Wellness Resort ist das einzige familiengeführte Boutique-Resort in Thailand, das auf Ayurveda-Retreats spezialisiert ist. Das Resort ist nur für Erwachsene (ab 12 Jahren) zugänglich und stolz darauf, Mitglied von Healing Hotels of the World zu sein und Gesundheitsurlaub in einer abgeschiedenen tropischen Umgebung anzubieten.
Erleben Sie die einzigartige Kombination der berühmten thailändischen Gastfreundschaft mit unserer Ayurveda-Expertise und einem professionellen Vollzeitteam aus Thailand und Indien.

Sonderpreise für Retreats und Unterkunft
Profitieren Sie von unserer Bestpreisgarantie und buchen Sie direkt hier!
🤩 Sonderangebote und Rabatte in der Nebensaison
🤩 Angebot für Langzeitaufenthalte
🤩 Frühbucherangebot
🤩 Zusätzlicher Rabatt bei höherer Anzahlung
🤩 Kostenlose Abholung vom Flughafen

AyurYoga Medic+
Ayurveda-Heilung mit nachweisbaren Ergebnissen
Für diejenigen, die auf der Suche nach einem wissenschaftlich fundierten traditionellen Heilretreat mit klassischem Ayurveda sind, kombiniert mit einer serologischen Laboranalyse zur nachweislichen Aufzeichnung der Ergebnisse.
Zusammenfassung des Retreats:
🌹 Mindestens 14 Nächte für beste und nachweisbare Ergebnisse
🌹 Bei An- und Abreise serologische Laboranalyse
🌹 Entwickelt und begleitet vom hauseigenen Arzt während der gesamten Retreat-Zeit
🌹 Etwa 2 Stunden tägliche Ayurveda-Behandlungen, 2 Stunden täglich Yoga, alle Mahlzeiten und Getränke inklusive
 AyurYoga Panchakarma Retreat
AyurYoga Panchakarma Retreat
Unser Team im Mangosteen Ayurveda & Wellness Resort brachte authentisches Ayurveda nach Thailand. Wir kombinieren ein fantastisches Urlaubserlebnis auf der wunderschönen Insel Phuket mit dem besten Ayurveda-Gesundheitsretreat, täglichem Yoga und gesunden Satvik-Mahlzeiten – angenehm und unvergesslich!
Zusammenfassung des Retreats:
🌺 Mindestens 7 Nächte erforderlich, 14 Nächte + empfohlen
🌺 Begleitung durch den hauseigenen Arzt während der gesamten Retreat-Zeit
🌺 Auf Ihre Bedürfnisse und Ziele zugeschnittenes Retreat-Programm
🌺 Etwa 2 Stunden täglich Ayurveda-Behandlungen
🌺 2 Stunden täglich Yoga, Zugang zur Himalaya-Steinsalz-Infrarotsauna
🌺 Alle gesunden Mahlzeiten und Getränke inklusive

Ananda Healing Retreat
Ayurveda – Reiki – Yoga – Meditation
Das Mangosteen Ananda Healing Retreat ist eine einzigartige Kombination aus mehreren authentischen Ayurveda-Behandlungen, Reiki-Heilsitzungen, Yoga, Meditation und Tempelbesuch sowie anderen interessanten, positiven Erlebnissen in der Natur!
Zusammenfassung des Retreats:
🌼 Mindestens 3 Nächte Retreat
🌼 Begleitung durch den hauseigenen Arzt während der gesamten Retreat-Zeit
🌼 Erleben Sie unseren erstklassigen Reiki-Meister
🌼 Sonnenaufgangsmeditation, Tempelbesuch, Ayurveda Behandlungen
🌼 Alle Mahlzeiten und Getränke inklusive

Burnout Prevention Retreat
Vorbeugung ist besser als Heilung!
🌻 7 Nächte / 8 Tage Burnout-Präventions-Retreat
🌻 360 Min. Spa-Behandlungen, 720 Min. Yoga & Meditation, 60 Min. Cardio oder Zumba, 2x Magnesiumbad, ca. 130 Minuten Wandern/Tempel = über 22 Stunden aktive Zeit und Spaß!
🌻 Es ist so toll, dass Sie Ihren Chef bitten können, es zu bezahlen 😂!
 Wellness Escape Retreat
Wellness Escape Retreat
4 Wellness-Ausflüge: „Vigor“, „Vitalize“, „Relax“ und „Toned“.
Permanente Wellness-Retreats mit 2 täglichen Yoga-Sitzungen!
🌷 Laufendes Yoga- und Wellness-Retreat mit täglichen Massagen in unserem einzigartigen Ayurveda-Spa. Buchen Sie beliebige Daten, 365 Tage im Jahr!
🌷 2 Stunden tägliches Yoga mit unseren erfahrenen Lehrern.
🌷 Mindestens 3 Nächte, aber bleiben Sie so lange, wie Sie möchten.

Mangosteen Pure Yoga Retreats
Nehmen Sie an Pure Yoga Retreats teil, beginnend mit einem Mindestaufenthalt von 3 Nächten.
🧘♂ Mangosteen Pure Yoga Retreats finden 365 Tage im Jahr statt!
🧘♂ Treten Sie jederzeit und an jedem Tag bei und bleiben Sie, solange Sie möchten. Wir organisieren Strand-Yoga-Sitzungen, Morgenwanderungen und andere Aktivitäten.
🧘♂ Ob fortgeschrittene Yogis oder Anfänger, wir haben den richtigen Kurs für Sie.